Insect Pest Management: A Key to Successful Farming
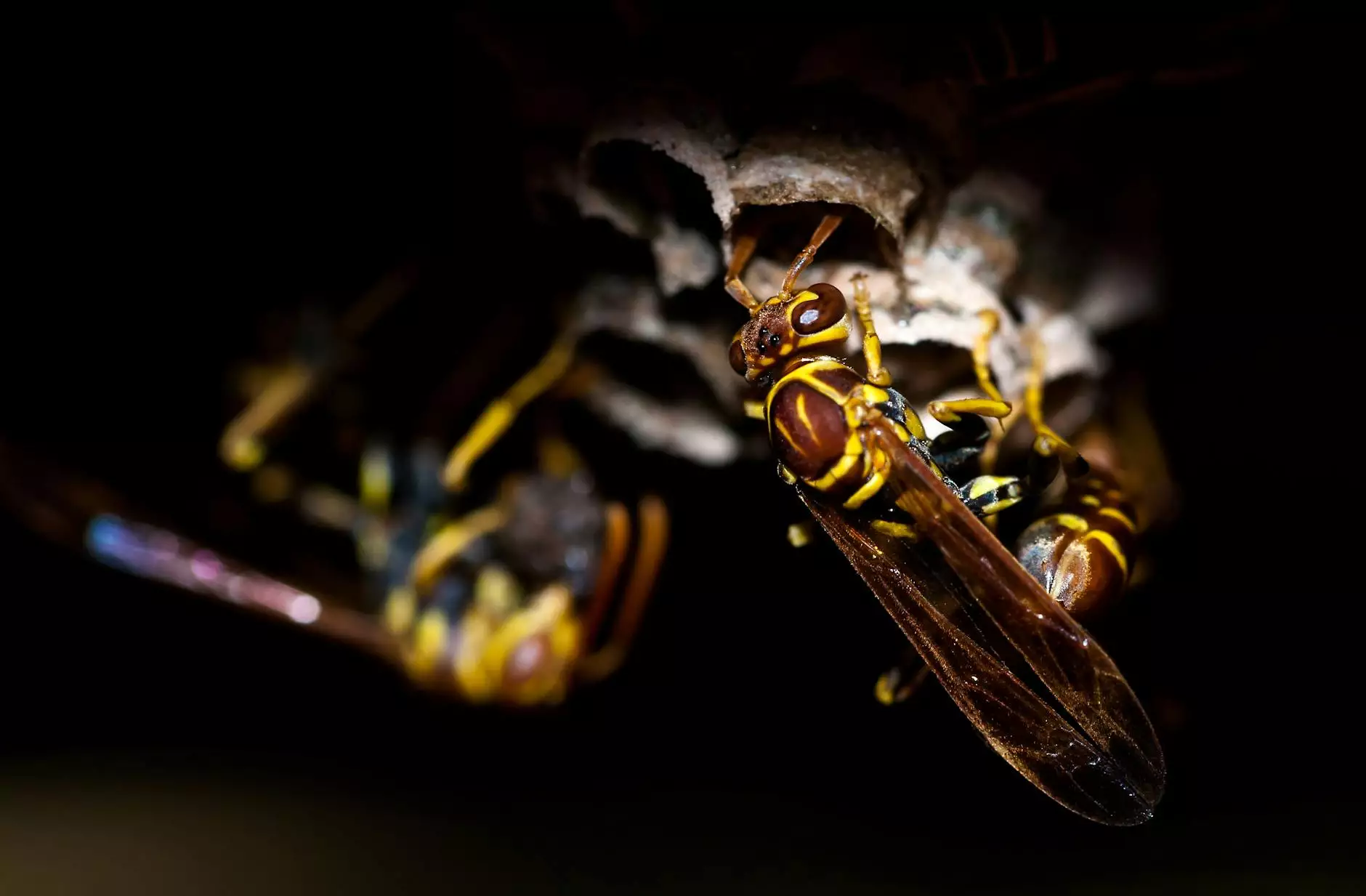

In the world of agriculture, insect pest management plays a crucial role in ensuring the health and productivity of crops. As farmers strive to maximize yield and maintain quality, understanding the intricacies of pest management becomes indispensable. This article delves deep into various strategies and approaches to effectively manage insect pests, ensuring a sustainable and successful farming operation.
Understanding Insect Pests and Their Impact on Agriculture
Insects can be both beneficial and harmful. While some species contribute to pollination and pest control, others can significantly damage crops, leading to financial losses. Here are the primary categories of insect pests that farmers encounter:
- Herbivorous Insects: These include aphids, caterpillars, and beetles that feed on plant tissues.
- Vectors of Disease: Some insects, like whiteflies and thrips, can transmit diseases to plants.
- Soil Pests: Grubs and root weevils can damage the roots of crops, hindering their ability to absorb nutrients and water.
Developing an Effective Insect Pest Management Plan
An effective insect pest management plan comprises several critical elements:
1. Identification of Pests
The first step in pest management is accurately identifying the insect species that pose a threat to crops. Farmers should regularly inspect their fields and utilize tools such as:
- Field scouting to observe and count pest populations
- Using pest identification charts or apps
- Engaging local extension services for expert advice
2. Monitoring Pest Populations
Monitoring is essential for understanding pest dynamics and assessing the need for control measures. This may include:
- Setting up traps to catch and count insects
- Utilizing weather data to predict pest outbreaks
- Recording pest life cycles to anticipate future infestations
3. Implementing Cultural Control Practices
Cultural control involves modifying farming practices to reduce pest establishment and survival. Effective strategies include:
- Crop Rotation: Alternating crops can disrupt pest lifecycles.
- Timing of Planting: Planting early or late can avoid peak pest populations.
- Sanitation: Cleaning up crop residues reduces overwintering sites for pests.
4. Biological Control Methods
Biological control employs natural enemies of pests to manage populations. This can include:
- Introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings
- Encouraging native predator species by creating habitats
- Using microbial pesticides derived from natural organisms
5. Chemical Control: When and How to Use Insecticides
While it's essential to use chemical control judiciously, insecticides can be effective when other methods fail. Key practices include:
- Choosing the appropriate insecticide based on the target pest
- Applying treatments at the right time for maximum effect
- Avoiding overuse and rotating chemicals to prevent resistance
Advantages of Implementing Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an innovative approach combining multiple pest control strategies for sustainable farming. The advantages of IPM include:
- Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides, leading to environmental benefits.
- Lower costs through efficient resource utilization.
- Increased crop resilience over time, promoting sustainable practices.
The Role of Technology in Insect Pest Management
As technology advances, farmers gain access to innovative tools that enhance insect pest management. Some significant technological advancements include:
- Drones: For aerial scouting and monitoring of large fields.
- Smart Sensors: Real-time data collection regarding pest presence and environmental conditions.
- Mobile Apps: Offering pest identification, treatment recommendations, and weather forecasts.
The Importance of Education and Resources
Staying informed is vital for successful pest management. Farmers should seek out resources such as:
- Local agricultural extension programs for up-to-date pest information
- Workshops and seminars on pest management strategies
- Online courses and webinars focusing on modern techniques
Conclusion: Making Insect Pest Management a Priority
The reality of modern agriculture is that insect pest management must be a priority for farmers aiming to optimize their production and sustainability. By understanding the types of pests, monitoring their populations, implementing a mix of control strategies, and leveraging technology and education, farmers can successfully navigate the challenges posed by insect pests.
Investing time and resources into developing a comprehensive pest management plan will not only enhance crop yields but also contribute to the overall health of the farm ecosystem. With the right practices in place, farmers can confidently protect their valuable crops while contributing to a sustainable agricultural future.